Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, also known as COPD, is a chronic and progressive (meaning it gets worse over time) lung disease that obstructs the airway making it difficult to breathe. While there is no cure for COPD, various treatments and lifestyle changes can help manage the symptoms and slow its progression. These may include quitting smoking, using bronchodilators and corticosteroids to open the airways and reduce inflammation, and engaging in pulmonary rehabilitation programs to improve lung function and quality of life.
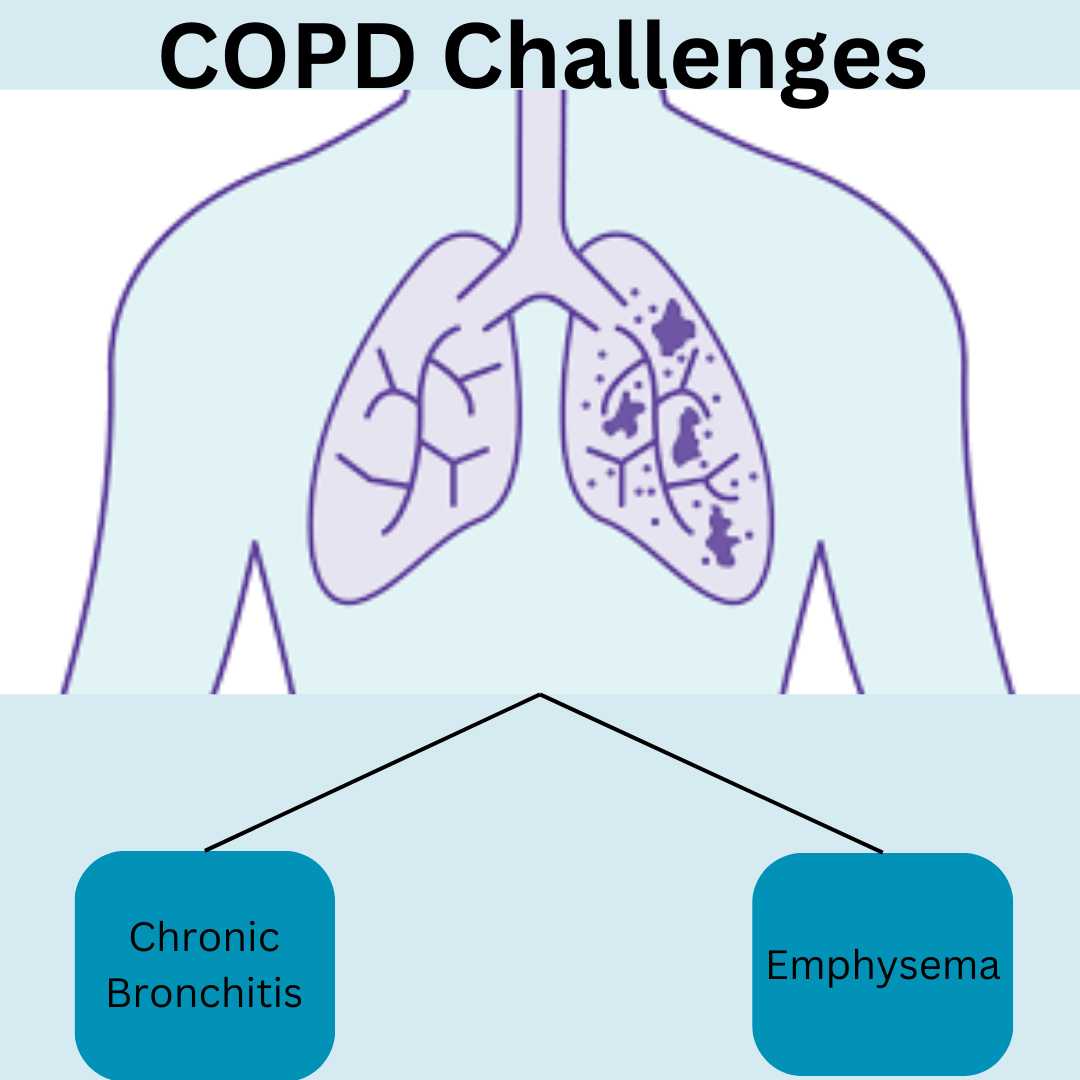
There are two main categories for COPD, chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
- Chronic Bronchitis: involves long-term inflammation of the bronchial tubes (the airways that carry air to the lungs), which leads to increased mucus production and a persistent cough.
- Emphysema: is a condition in which the air sacs in the lungs (alveoli) are gradually destroyed. This reduces the surface area available for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs.
Symptoms of COPD may include shortness of breath, coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and increased production of mucus. These symptoms typically worsen over time and can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life and overall health.
Daily challenges of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease:
- Breathing Difficulties: Shortness of breath is a hallmark symptom of COPD. This can make even simple tasks like walking, climbing stairs, or carrying groceries feel exhausting and difficult.
- Chronic Cough: A persistent, chronic cough is common in COPD. It can be not only physically uncomfortable but also socially and emotionally challenging.
- Mucus Production: Many people with COPD produce excess mucus, which can lead to frequent throat clearing and coughing. This can be socially embarrassing and physically uncomfortable.
- Limited Physical Activity: Due to breathlessness and fatigue, people with COPD may find it difficult to engage in physical activities. This can lead to reduced fitness levels and contribute to a sedentary lifestyle.
- Medication Management: COPD often requires daily medication management, which can be complicated, especially when multiple medications are involved.
- Oxygen Therapy: In advanced stages of COPD, individuals may require supplemental oxygen therapy, which can be cumbersome to carry and manage.
- Anxiety and Depression: The chronic nature of the disease, along with the physical limitations it imposes, can lead to feelings of anxiety and depression. These emotional challenges can further affect a person’s quality of life.
- Social Isolation: Some people with COPD may limit their social interactions or activities due to the fear of breathlessness, which can lead to social isolation and reduced quality of life.
- Diet and Nutrition: Maintaining a healthy diet can be challenging for those with COPD. Poor appetite, difficulty eating, and the need for energy-conserving techniques can impact nutritional intake.
- Medical Appointments: Managing COPD often requires frequent medical appointments, which can be time-consuming and sometimes physically demanding.
- Environmental Considerations: Avoiding exposure to irritants like smoke, air pollution, and dust becomes crucial for managing COPD.
- Weather Sensitivity: Extreme temperatures, humidity, or air quality fluctuations can impact COPD symptoms, making it necessary to be cautious about environmental conditions.
- Financial Burden: COPD management, including medications and oxygen therapy, can be expensive and may place a financial burden on individuals and families.
Coping with these daily challenges often requires a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, emotional support, and self-management strategies. People with COPD can benefit from a healthcare team that includes doctors, respiratory therapists, and counselors, as well as support from friends and family. Education about the disease and learning techniques to manage symptoms can help individuals improve their quality of life and effectively address the daily challenges that COPD presents.
So, what is COPD caused by?
COPD is often caused by long-term exposure to irritants, such as cigarette smoke being the most common. Other factors, such as exposure to air pollution, dust, and chemical fumes, can also contribute to the development of COPD. An early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential for someone with COPD.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of COPD, it is important to seek medical advice and evaluation from a healthcare professional. You can also request information regarding BTC of New Bedford’s enrolling clinical trial for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Learn more about the trial here.